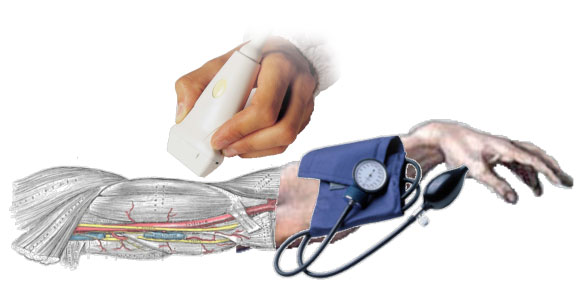
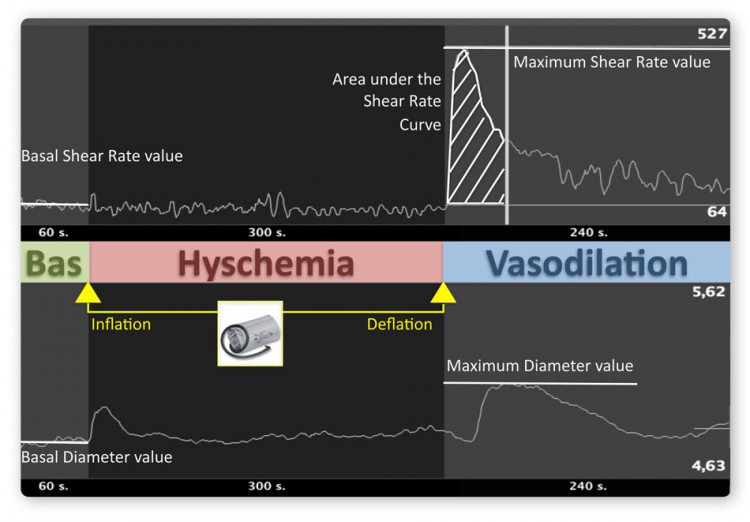
After 60 seconds, the pressure cuff is inflated to induce a 5 minutes long of artificial hyschemia; and then, simply releasing the cuff, you could observe the reactive hyperemia: by this way, a big amount of blood will flow through the vessel inducing a shear stress on the vessel wall.
A shear stress applied on the internal surface of an artery induces a chemical endothelium response (nitric oxide), that in turn, induces a vasodilation of the artery.
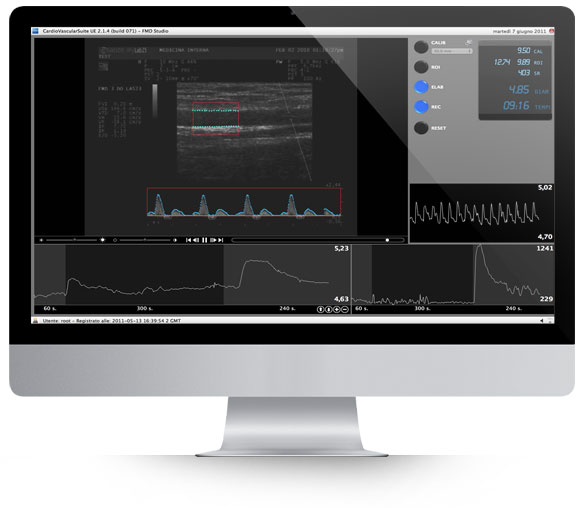
The sonographer will record the percentage of vasodilation relating to basal value and link it to the shear stress calculated through blood flow velocity acquired through the Doppler ultrasound in duplex mode.
The FMD percentage is the difference between the maximum value of the diameter and the mean baseline diameter and it’s strictly correlated to endothelial dysfunction: